
"Sortable list of elements of the Periodic Table".
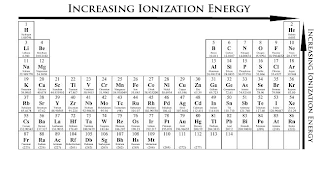
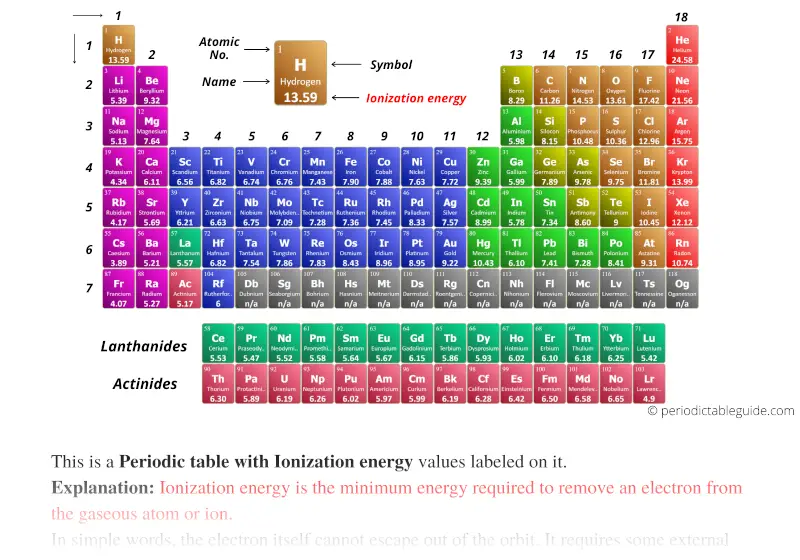
The story behind the discovery that elements are born in stars. Atomic Weights of the Elements (From IUPAC). Multilingual Dictionary and Etymology of the Periodic Table Elements. Atomic Reference Data for Electronic Structure Calculations. List of Periodic Table Elements in Hebrew. Other resources related to the Periodic Table Thus, alkali metals have the lowest IE in a period and, Rare gases have the highest. IE decreases going down a column of the periodic table, and increases from left to right in a row. Reference: NIST Reference Table on Ground states and ionization energies for the neutral atoms. To convert to kJ/mol, multiply by 96.4869. The table lists only the first IE in eV units. Ionization energy (IE): The energy required to remove the outermost electron from an atom or a positive ion in its ground level. For these elements, the weight value represents the mass number of the longest-lived isotope of the element.Įlectron configuration: See next page for explanation of electron configuration of atoms. The elements marked with an asterisk have no stable nuclides. The values shown here are based on the IUPAC Commission determinations ( Pure Appl. For relative abundances of isotopes in nature, see reference on Atomic Weights and Isotopic Compositions.Ītomic weight: Atomic weight values represent weighted average of the masses of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element. The abundance of each isotope depends on the source of materials. For example, the two common isotopes of carbon, 12C and 13C, have 6 and 7 neutrons, respectively. Elements have more than one isotope with varying numbers of neutrons. 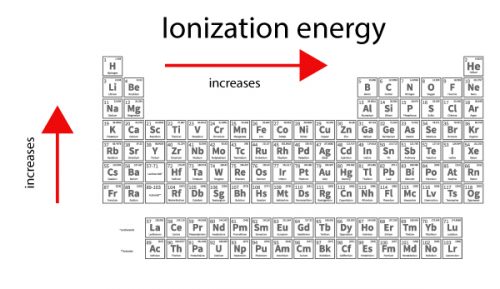
The isotope of an element is defined by the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus.
Isotope: Atoms of the same element with the same atomic number, but a different number of neutrons.
Thus, each proton and neutron has a mass of about 1 amu. This isotope of carbon has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. Atomic mass is measured in Atomic Mass Units (amu), which are scaled relative to carbon, 12C, that is taken as a standard element with an atomic mass of 12. Each element is uniquely defined by its atomic number.Ītomic mass: The mass of an atom is primarily determined by the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. boiling pointĪtomic number: The number of protons in an atom. For the Year of Discovery of each elements see the list with the English and Hebrew names.For these elements, the weight value shown represents the mass number of the longest-lived isotope of the element. The elements marked with an asterisk (in the 2nd column) have no stable nuclides.Lanthanoids and Actinoids are numbered as 101 and 102 to separate them in sorting by group. Group: There are only 18 groups in the periodic table that constitute the columns of the table.List of Periodic Table elements - Ionization energy No.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
